The Self-Attention Mechanism
The Multihead attention
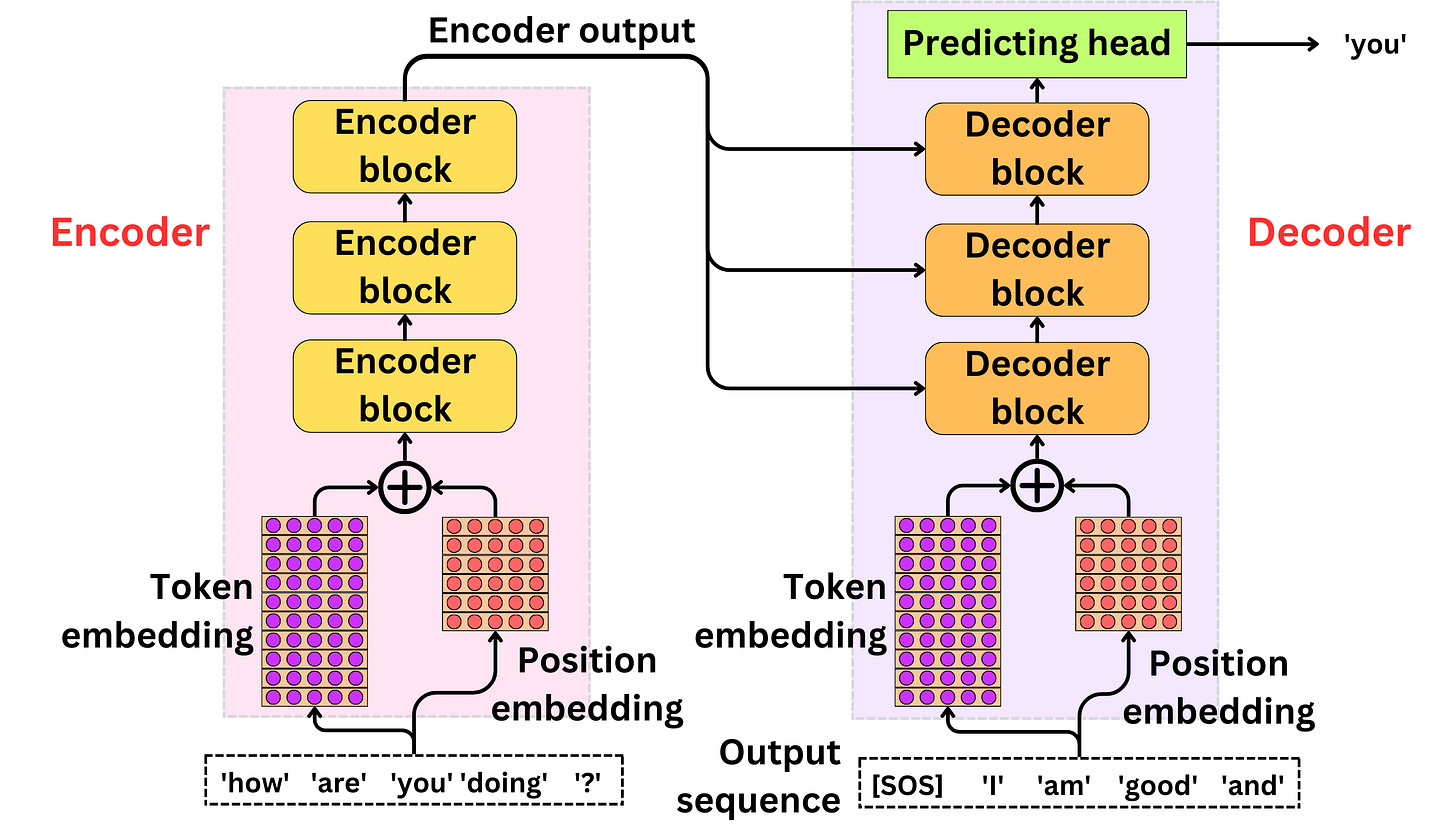
The encoder
The decoder
The position embedding
The encoder block
The self-attention layer
The layer-normalization
The position-wise feed-forward network
The decoder block
The cross-attention layer
The predicting head
The overall architecture
The architecture is composed of an encoder and a decoder.
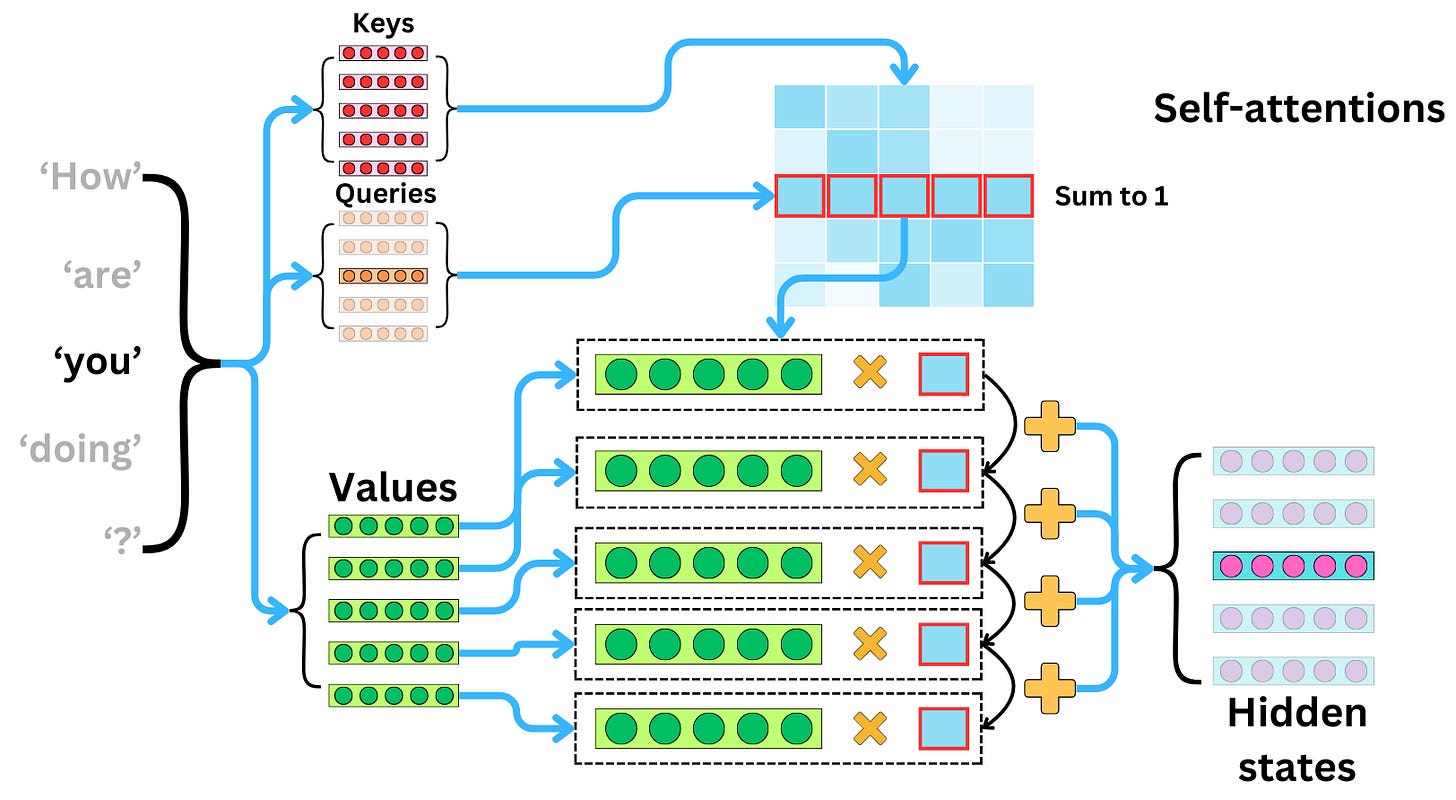
The self-attention layer
The self-attentions are used to replace the recurring units to capture the interactions between words within the input sequence and within the output sequence.
In the self-attention layer, we first compute the keys, queries, and values vectors.
We then compute the matrix multiplication between the keys and queries.
After a softmax transformation, this matrix of interactions is called the attention matrix. The resulting output hidden states of the attention layer are the matrix multiplication of the attention matrix and the values vectors.
Each of the resulting hidden states coming from the attention layer can be understood as a weighted average of the values, with the attentions being the weights.
The multi-head attention layer
Using multiple attention layers in parallel helps capture different interactions between the words of the input sequence. The dimension of the of the hidden states coming out of each attention head is divided by the number of heads and concatenated to the other hidden states. The resulting hidden states are combined into final hidden states using a linear layer.
To reduce the dimensionality of the hidden states, we just need to change the shape of the internal matrices:
The position embedding
The position embedding is used to add the position information to the semantic information of the words.